Unitronics PLC interfacing
RJ11 serial RS232 and RS485 connections
Unitronics is a PLC-manufacturer based in Israel. For communications, many of their products are equipped with an RS232 or RS485 serial port. These ports use an RJ11 socket as physical connector. The RJ11 connector can be used for both RS232 and RS485. The actual functionality is determined by DIP-switches on the mainboard of the PLC.
The RJ11 socket is interesting, because the manufacturer choose to have a symmetrical pin-layout, just as with the MMJ connector on DECconnect systems and the RJ45 jack in the Yost standard. A symmetrical pin-layout allows two DTEs, data terminal equipment, to be connected directly without use of a modem or other DCE, data communication equipment. It shouldn’t however be a surprise that the pin assignment on the RJ11 socket on Unitronics PLCs is different from the two systems mentioned above. The existence of an RS485 port on the socket makes it even a little bit more difficult. When in full RS232 mode, the six available pins are assigned to the most used RS232 signals. Pin 1 and 6 however are reassigned to the A and B lines when the port is used in RS485 mode. These pins are normally used for the DTR, data terminal ready and DSR, data set ready signals. On some PLC models it is possible to mix RS232 and RS485 communications. When the DSR and DTR signals are not used, the two pins can be used for simultaneous RS485 communication.
Unitronics PLC pin assignment for the RJ11 socket
The RJ11 socket in the Unitronics PLCs provides six signal pins. In RS232 mode all pins are used for RS232 signals. When in RS485 mode, only in 1 and 6 are reassigned. The central four pins remain their original RS232 functionality.
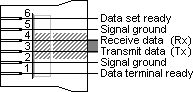
| Pin | RS232 function | RS485 function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | DTR | A (+) |
| 2 | Signal ground | RS232 signal |
| 3 | TxD | RS232 signal |
| 4 | RxD | RS232 signal |
| 5 | Signal ground | RS232 signal |
| 6 | DSR | B (-) |
Basic Unitronics RJ11 connection cables
The symmetrical pin layout of the RJ11 sockets on the Unitronics PLCs allows an easy way of interconnecting the PLCs with both RS232 and RS485 communications. For RS232 a crossover cable is used where pin 1 is connected with pin 6 at the other connector, pin 2 with pin 5, etc. This interconnects the transmit and receive signals of both PLCs, and also the handshaking signals DTR and DSR. If handshaking is not necessary, an ordinary 4 wire telephone cable could be used, provided that the pins are cross-connected as shown in the picture below. Otherwise a full 6 wire cable must be used. Two wire telephone cables will not function because in that case the ground signal levels on both sides will be floating.
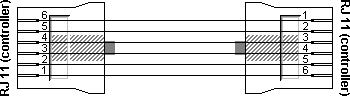
| RJ11 plug 1 | RJ11 plug 2 | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | DTR ► DSR |
| 2 | 5 | Signal ground |
| 3 | 4 | TxD ► RxD |
| 4 | 3 | RxD ◄ TxD |
| 5 | 2 | Signal ground |
| 6 | 1 | DSR ◄ DTR |
RS485 is in its design a different interface from RS232. The RS485 interface allows the creation of multi-point networks. The normal way to implement this is with a two wire system with differential signal levels. These signals are commonly called A and B in RS485 systems. The A signals of all devices should be connected with each other and the same goes for the B signals. Therefore for RS485 communications no crossover cable is used. To prevent noise to interfere with the communications, often twisted pair cable is used. The diagram below shows a basic RS485 cable for use with the RJ11 socket on Unitronics PLCs. You can easily connect more devices by splitting the cable at one connector and adding another cable to it.
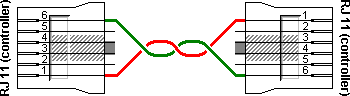
| RJ11 plug 1 | RJ11 plug 2 | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | A (+) ◄ ► A (+) |
| 6 | 6 | B (-) ◄ ► B (-) |
RS232 to Unitronics RJ11 PC programming cables
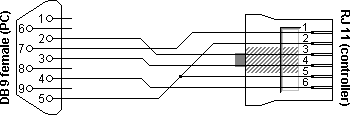
PCs are normally not equipped with an RJ11 socket for serial RS232 communications. If we want to connect a PC with an Unitronics PLC, for example for programming or debugging reasons, we need a connection cable which is on one side fitted with a female DB9 connector, and on the other side with an RJ11 jack. The layout for this cable is shown below.
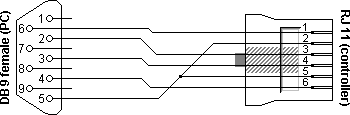
| DB9 | RJ11 | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | RxD ◄ TxD |
| 3 | 4 | TxD ► RxD |
| 4 | 6 | DTR ► DSR |
| 5 | 2 + 5 | Signal ground |
| 6 | 1 | DSR ◄ DTR |
The Jazz PLC series from Unitronics are not standard equipped with a RJ11 connector for serial communications. The only way to add RS232 capabilities to the Jazz PLCs is by using the MJ20-PRG programming port add-on module. This MJ20-PRG module clicks in the PLC and provides one RJ11 socket for serial communications with a PC. This module is powered by the RS232 port from the connecting computer. Therefore the pin assignment is a little bit different from the default pin assignment on the RJ11 socket. The main difference is, that pin 1 and 6 on the RJ11 socket of the MJ20-PRG module are used as power supply. These pins have to be connected to handshaking outputs at the PC side on the RS232 port. Normally pin 7 (RTS) and pin 4 (DTR) are used on the DB9 connector.
| DB9 | RJ11 | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | RxD ◄ TxD |
| 3 | 4 | TxD ► RxD |
| 4 | 6 | DTR ► Power |
| 5 | 2 + 5 | Signal ground |
| 7 | 1 | RTS ► Power |
|
In any series of calculations,
errors tend to occur at the opposite end
from the end at which you begin checking for errors.
GRELB'S LAW OF ERRORING
|